Countries Should Set Way to Identify Users of Banned Weapon
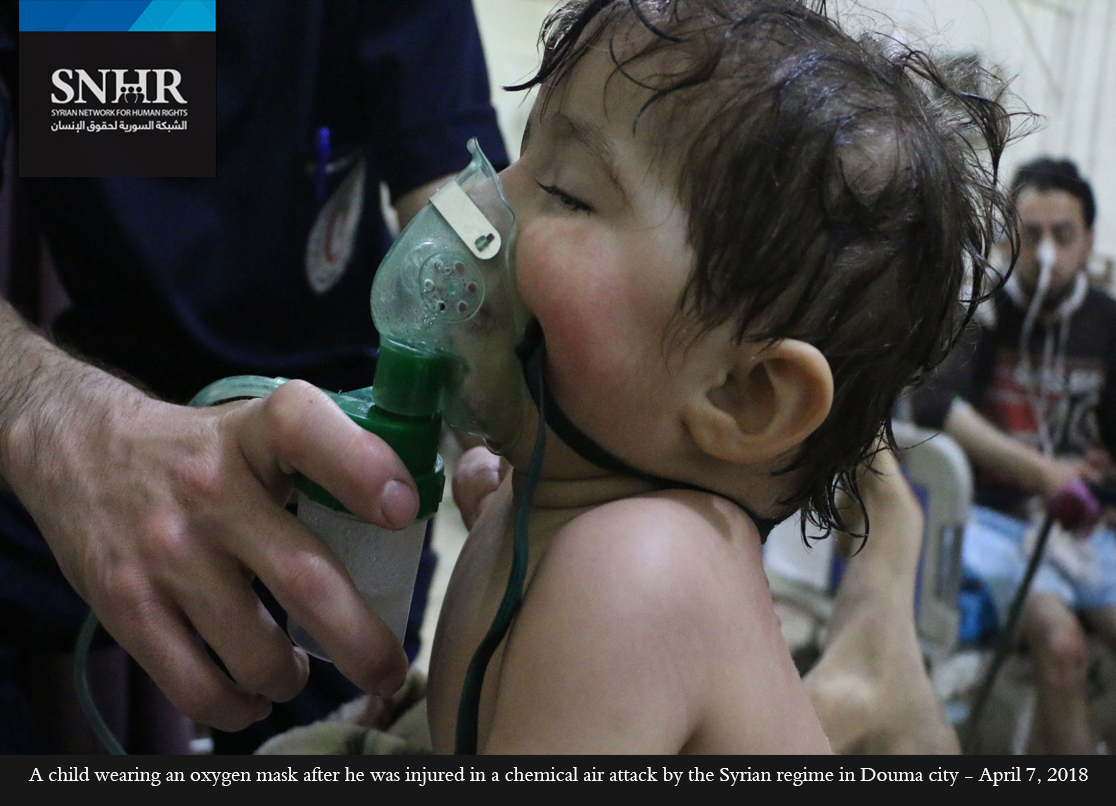
(New York, June 19, 2018) – Governments should strengthen the tools to reverse the unprecedented threat to the global ban on chemical weapons, a coalition of 21 human rights and humanitarian groups said today. The continuing unattributed use of chemical weapons in Syria and nerve agents in the United Kingdom and Malaysia highlight the need to assign responsibility for those violating the longstanding and near universally accepted prohibition against chemical weapons.
On June 26, 2018, the 192 members of the 1992 Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC) will have the opportunity to strengthen compliance with one of the most adhered-to weapons bans in history when they gather for a special meeting in The Hague. The meeting, requested by 11 states parties, aims to take urgent steps to strengthen the implementation of the convention. This should include ensuring that the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) can attribute responsibility for chemical attacks in Syria and anywhere else they take place.
“The June 26 meeting is an important opportunity for member countries to reaffirm their commitment to the Chemical Weapons Convention and strengthen it,” said Sherine Tadros, head of the New York office of Amnesty International. “All states parties should come to The Hague and vote to create a team to clearly identify who is violating the treaty’s core prohibition on using chemical weapons.”
Many member states do not have permanent representatives assigned to the OPCW headquarters in The Hague. However, all governments should make attending the meeting and strengthening the ban a priority, the groups said.
The continuing use of chemical weapons in Syria is the biggest threat to the viability of the convention, the groups said. Over 85 confirmed chemical attacks have taken place in the country since August 21, 2013, the day of the deadliest chemical attack in Syria to date, at least 50 of them by Syrian government forces, based on research by the United Nations, Human Rights Watch, Amnesty International, and other organizations. Chemical weapons are inherently indiscriminate, and using them constitutes a war crime. Until November 2017, the UN and the OPCW Joint Investigative Mechanism (JIM) was authorized to identify who was responsible for chemical attacks in Syria. But after the JIM found the Syrian government responsible for the April 2017 sarin attack in Khan Sheikhoun, Russia used its veto in the UN Security Council to prevent the renewal of the JIM’s mandate.
“The threat of Russia’s veto looms large over any Security Council action for a credible procedure for attributing blame,” said Simon Adams, Executive Director of the Global Center for the Responsibility to Protect. “Member states should empower the OPCW to urgently fill this gap to help ensure the Chemical Weapons Convention is not undermined further.”
As a first step, states parties should ask the OPCW to take on the task of identifying those responsible for using chemical weapons in Syria. However, if the June meeting fails to successfully achieve this goal, UN Secretary-General António Guterres should immediately appoint a team of experts who could do so. The lack of attribution of responsibility fuels a cycle of impunity for these attacks and emboldens parties to the conflict to continue the use of chemical weapons in Syria.
The situation in Syria is emblematic of a wider problem with the OPCW’s capacity to ensure compliance with the Chemical Weapons Convention. It can send fact-finding missions to determine whether chemical weapons have been used but remains unable to attribute responsibility for their use. To better ensure that warring parties responsible for their use can be held to account, the convention’s member countries need a credible way to identify those involved in chemical warfare.


